Engineering Molding
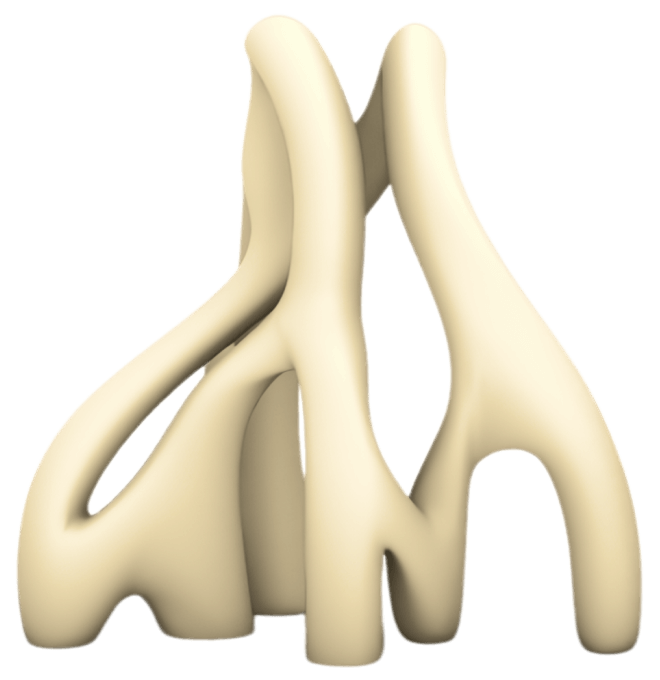
3D Printing in Engineering and Molding
Uses
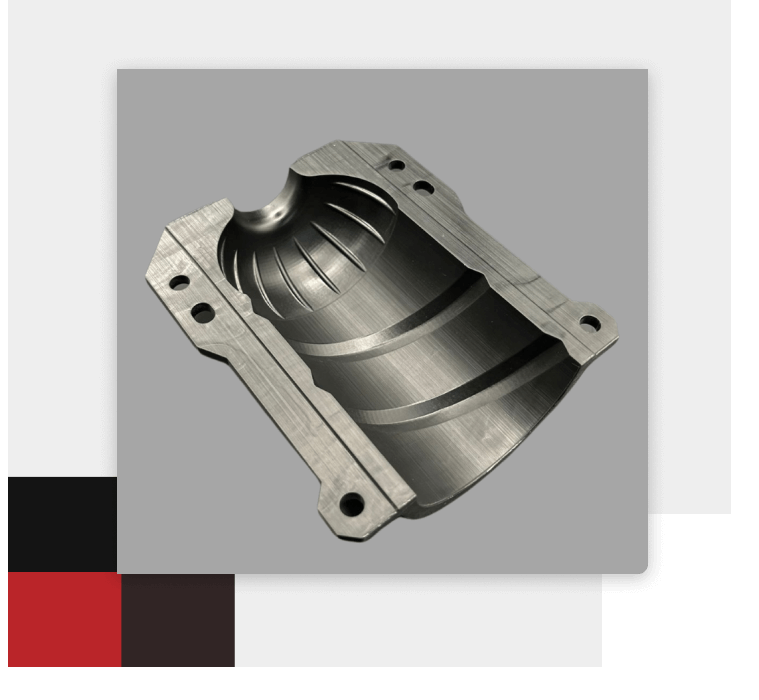
High-Precision Industrial Molds:
Used to design molds for injection and casting of metals and plastics, enhancing industrial production quality.
Prototyping:
Enables the creation of precise prototypes to test designs before large-scale manufacturing.
Spare Parts and Complex Structures:
Ideal for producing custom parts for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and energy.

Method
3D Digital Design (3D CAD):
The process begins with creating the mold design using advanced engineering software.
Printing with Specialized Materials:
Suitable materials (like resins or durable plastics) are selected based on requirements for precision and durability.
Finishing and Processing:
Printed molds can be enhanced with post-processing techniques like polishing or coating.

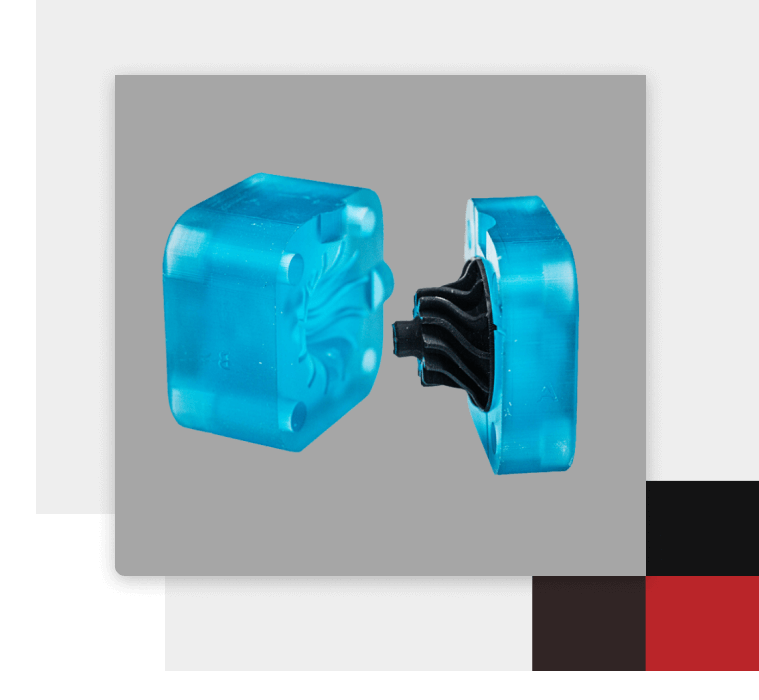
Advantages
Exceptional Precision:
Produces detailed and complex geometries that are unattainable with traditional methods.
Time and Cost Savings:
Reduces production time and tooling costs compared to conventional manufacturing techniques.
Design Flexibility:
Allows easy modifications to designs and the production of various sizes and shapes without changing tools.
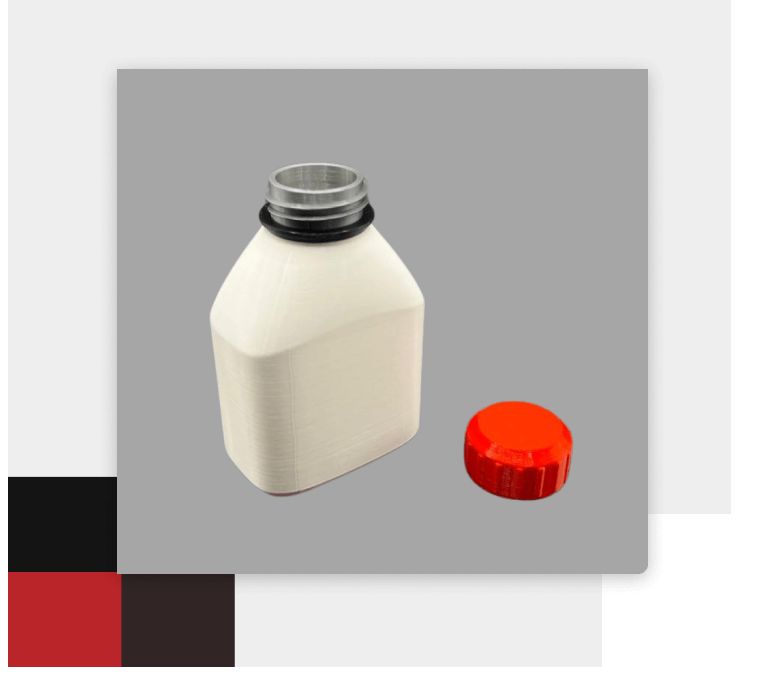
Revolutionize Your Engineering Workflow
This advanced technological solution gives you the ability to transform your engineering ideas into tangible realities quickly and efficiently.
Get in Touch
Wed love to hear from you! Whether you have a question, need support, or want to explore how we can work together, we're here to help. Let's start a conversation!